A participatory system dynamics model to investigate sustainable urban water management in Ebbsfleet Garden City
| dc.contributor.author | O'Donnell, Emily | |
| dc.contributor.other | Pluchinotta, Irene | |
| dc.contributor.other | Pagano, Alessandro | |
| dc.contributor.other | Vilcan, Tudorel | |
| dc.contributor.other | Ahilan, Sangaralingam | |
| dc.contributor.other | Kapetas, Leon | |
| dc.contributor.other | Maskrey, Shaun | |
| dc.contributor.other | Krivtsov, Vladimir | |
| dc.contributor.other | thorne, colin | |
| dc.coverage.spatial | Ebbsfleet Garden City, Kent, UK | en_UK |
| dc.coverage.temporal | Modelling from 2019 until 2049 | en_UK |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2021-01-13T08:30:30Z | |
| dc.date.available | 2021-01-13T08:30:30Z | |
| dc.date.issued | 2021-01-13 | |
| dc.identifier.uri | https://rdmc.nottingham.ac.uk/handle/internal/8302 | |
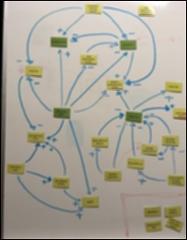
| dc.description.abstract | Growing urban populations, changes in rainfall patterns and ageing infrastructure represent significant challenges for urban water management (UWM). There is a critical need for research into how cities should adapt to become resilient to these impacts under uncertain futures. UWM challenges in the Ebbsfleet Garden City (UK) were investigated via a participatory process and potential sustainable solutions were explored using a System Dynamics Model (SDM). Collaborative development of the SDM by the Ebbsfleet Learning and Action Alliance developed stakeholders’ understanding of future UWM options and enabled a structured exploration of interdependencies within the current UWM system. Discussion by stakeholders resulted in a focus on potable water use and the development of the SDM to investigate how residential potable water consumption in the Ebbsfleet Garden City might be reduced through a range of interventions, e.g., socio-environmental and economic policy incentives. The SDM approach supports decision-making at a strategic, system-wide level, and facilitates exploration of the long-term consequences of alternative strategies, particularly those that are difficult to include in quantitative models. While an SDM can be developed by experts alone, building it collaboratively allows the process to benefit from local knowledge, resulting in a collective learning process and increased potential for adoption. | en_UK |
| dc.language.iso | en | en_UK |
| dc.publisher | The University of Nottingham | en_UK |
| dc.relation.uri | http://www.urbanfloodresilience.ac.uk/learning-and-action-alliances/ebbsfleet-laa.aspx | en_UK |
| dc.rights | CC-BY | * |
| dc.rights.uri | https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ | * |
| dc.subject.lcsh | Municipal water supply | en_UK |
| dc.subject.lcsh | Garden cities | en_UK |
| dc.subject.lcsh | Water-supply -- England -- Ebbsfleet Garden City | en_UK |
| dc.subject.lcsh | Water-supply -- Mathematical models | en_UK |
| dc.title | A participatory system dynamics model to investigate sustainable urban water management in Ebbsfleet Garden City | en_UK |
| dc.identifier.doi | http://doi.org/10.17639/nott.7042 | |
| dc.subject.free | Group Model Building, Collaborative Decision Making, Ebbsfleet Garden City, Integrated Water Management, System Dynamics, Stakeholders | en_UK |
| dc.subject.jacs | Engineering::Others in engineering | en_UK |
| dc.subject.lc | G Geography. Anthropology. Recreation::GE Environmental Sciences | en_UK |
| dc.date.collection | June 2019-March 2020 | en_UK |
| uon.division | University of Nottingham, UK Campus::Faculty of Social Sciences::School of Geography | en_UK |
| uon.funder.controlled | Engineering & Physical Sciences Research Council | en_UK |
| uon.datatype | Excel spreadsheet detailing scenarios run through a System Dynamics Model to investigate sustainable urban water management in the Ebbsfleet Garden City | en_UK |
| uon.grant | EP/P004180/1 | en_UK |
| uon.parentproject | Achieving Urban Flood Resilience in an Uncertain Future | en_UK |
| uon.collectionmethod | Scenarios created by a System Dynamics Model, run in Vensim® Software (by Ventana Systems). | en_UK |
| uon.rightscontact | Irene Pluchinotta (lead author) | en_UK |
| uon.preservation.rarelyaccessed | true |
Files in this item
This item appears in the following Collection(s)
-
Public Research Data
A collection of research data, held in this repository, that is publicly available, except where individual embargoes apply